
The sequencing costs were funded by the Belfast Health and Social Care Trust and the COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) Consortium, which is supported by funding from the Medical Research Council (MRC) part of UK Research & Innovation (UKRI), the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) and Genome Research Limited, operating as the Wellcome Sanger Institute.Īdditional funding was provided by Public Health England (PHE). The authors have declared no competing interest. Our generalisable methodology to study introduction dynamics and optimal sequencing levels will assist public health authorities to select the most appropriate control measures and viral sequencing strategy. However, there were similar rates of Delta infection within NI and RoI, suggesting that although travel restrictions will reduce risk of introducing novel variants to the region, they may not substantially decrease total incidence. This approach showed similar rates of introductions for all major lineages into Northern Ireland (NI) and Republic of Ireland (RoI) with the exception of Delta, which was higher in NI which is likely attributable to higher travel per capita. Per capita normalisation of both sequencing levels and detected introductions accounts for biases due to differing sequencing efforts and total populations. By downsampling, we estimate the power to detect introductions to Ireland as a function of sequencing levels.

This mirroring of the phylogenetic relationships by the geospatiotemporal propagation of SARS-CoV-2 validates our analytic approach. When introduction cluster samples are mapped sequentially by collection date, they appear predominantly in previously affected or adjacent areas. The clusters of sequences predicted to derive from discrete introduction events (“introduction clusters”) vary greatly in size, with some involving only one or two cases and others comprising thousands of samples. The majority of SARS-CoV-2 introductions originated from England, with frequent introductions from USA and northwestern Europe. Using phylogenomic analysis incorporating sample collection date and location metadata, we describe multiple introduction and spreading events for all major viral lineages to the island of Ireland during the period studied (March 2020–June 2022). Furthermore, the two distinct political jurisdictions on the island allow comparison of the impact of varying public health responses on viral dynamics, including SARS-CoV-2 introduction events. Because Ireland is an island, accurate documentation of travel rates to and from other regions, both by air and by sea, are available. High levels of WGS have enabled effective SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance on the island of Ireland, leading to the generation of a sizeable data set with potential to provide additional insights into viral epidemiology.
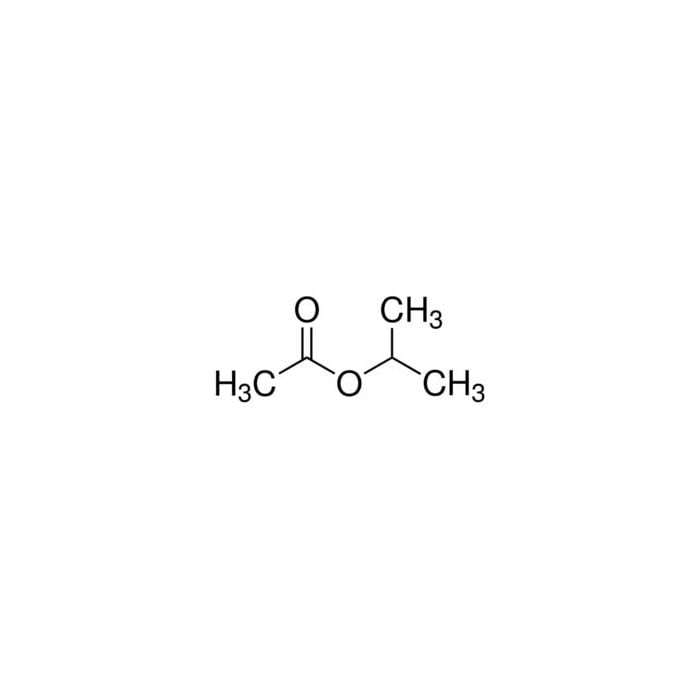
Viral whole-genome sequencing (WGS) has provided insights into SARS-CoV-2 molecular mechanisms of pathogenicity and evolution and contributed to the development of anti-virals and vaccines. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has had an unprecedented impact on the people of Ireland as waves of infection spread across the island during the global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
